Refrigeration cycles form the cornerstone of how refrigerators and air conditioning systems operate, delineating their thermodynamic processes. Among these, four primary types stand out
Vapor Compression Refrigeration Cycle
This widely adopted method orchestrates the compression of a refrigerant gas, followed by its condensation into a liquid state. Subsequently, controlled expansion reduces pressure and temperature, leading to evaporation, where heat absorption cools the intended space.
Absorption Refrigeration Cycle
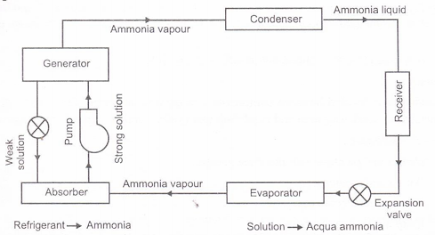
Operating on a different principle, this cycle harnesses a heat source to induce the evaporation of a refrigerant from a solution. Its domain extends beyond conventional systems, finding favor in industrial setups and expansive refrigeration frameworks.
Employing air as the refrigerant, this cycle, while less efficient than its vapor compression counterpart, occupies a niche in aircraft cooling apparatus and select industrial configurations.
Gas Refrigeration Cycle
Distinguished by its use of alternative gases like carbon dioxide or ammonia as refrigerants, this cycle caters to specialized industrial demands and environmental considerations that dictate unconventional cooling solutions.
These distinctive refrigeration cycles each boast unique attributes, serving varied needs across industries while navigating their respective advantages and drawbacks



Comments
Post a Comment